Trans Fat | Environmental Health

Foods high in Trans Fat cause heart disease. Refer to the Trans Fat facts document to find out more.
Restaurants and grocery stores that prepare food may not use partially hydrogenated vegetable oils, shortenings, or margarine for frying, pan frying, or grilling; or as a spread, unless you have product labels or other documents from the manufacturer showing that these ingredients contain less than 0.5 grams of trans fat per serving.
Restaurants and grocery stores that prepare food may not use partially hydrogenated vegetable oils, shortenings, or margarine that contain more than 0.5 grams trans fat per serving. This will include oils and shortenings used for deep frying of yeast or cake batter.
This regulation does not apply to food that is served directly to patrons in the manufacturer’s original, sealed packaging, such as a package of crackers or a bag of potato chips.
The regulation requires that at least one sign must be posted at each entrance to an eating and drinking establishment indicating the eating and drinking establishment complies with the requirements of this regulation.
| Menu Labeling Documentation | Format |
|---|---|
| Trans Fat Facts |
Helpful Trans Fat Resources
Montgomery County Council Resolution 16-134
Required Signs (PDF for download)
Understanding Nutrition Facts
For assistance with services, email [email protected]
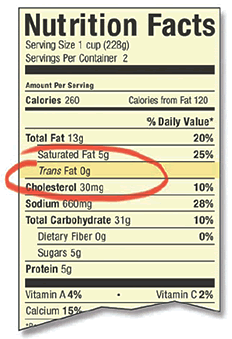

Check the Label for Trans Fat
- Check for Trans Fat Keywords:
Look at the package label or ingredients list to see if " partially hydrogenated," "shortening," or " margarine" are listed. If none of these terms appear, you may use the product.
If any of these terms are listed, go to Step 2 to see if the product contains too much trans fat.
- Check for Trans Fat:
Check the nutrition facts panel for trans fat content. If the panel says the product has 0 grams of trans fat, or less than 0.5 grams of trans fat per serving, you may use the product.
If the nutrition facts panel says the product has 0.5 grams or more trans fat, you may not use the product.
If there is no nutrition facts panel on the product, go to Step 3.
- No Nutrition Facts:
If there is no nutrition facts panel, ask your supplier to provide a letter from the manufacturer listing the product's ingredients. If the ingredients list contains the words " partially hydrogenated," " shortening," or " margarine," the letter must also include information on the amount of trans fat in each serving.
As in Step 2, if the product has 0 grams of trans fat, or less than 0.5 grams of trans fat per serving, you may use it.
The letter should be on the manufacturer’s letterhead and show the manufacturer’s name and address. Keep the letter at your food service establishment, available for review by a Department of Health and Human Services inspector.
Visit the FDA Site for more information on product labels.
Good fats & where to find them
"Good Fats help you protect your heart by maintaining levels of "good" HDL cholesterol while reducing levels of "bad" LDL cholesterol in your blood. Good fats such as Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated fats lower your risk of heart disease."
Types of Good Fat :
1. Monounsaturated Fat: this "healthy fat" is rich in Vitamin EWhere can Monounsaturated Fats be found:
- Olives
- Olive and canola oils
- Cashews, almonds, peanuts, and most other nuts
- Avocados
- Corn, soybean, safflower, sunflower and cottonseed oils
- Fish and seafood
To find out more about the benefits of Polyunsaturated Fat and Monounsaturated Fat visit the American Heart Association's website .
Bad fats & where to find them
"Bad fats such as Saturated and Trans fats increase your risk of heart disease."
Types of Bad Fats :
1. Saturated Fats and Trans Fats can increase the risk of heart disease, raise LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein).Where can Saturated Fats be found:
- Whole milk, butter, cheese and ice cream
- Lard and suet
- Meat (beef, pork, bacon, sausage and deli meats have the most)
- Chicken and other poultry have less, especially with the skin removed
- Chocolate and cocoa butter
- Palm oil
- Coconut products, including milk and oil
- Partially hydrogenated vegetable oil
- Many margarine and shortenings
- Many deep-fried foods
- Many fast foods
- Many store-bought baked goods
To find out more about Trans Fats and Saturated Fats, visit the American Heart Association website .
To find out more about the benefits of Polyunsaturated Fat and Monounsaturated Fat visit the American Heart Association on the web.