
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is the most common form of Diabetes. In 2019, diabetes was the 7th leading cause of death in Montgomery County, and the 5th leading cause of death in men between 2017 and 2019. Seven percent of adults aged 18 years and older have been told that they have diabetes in the county, compared to 10% in Maryland. Emergency Room (ER) visits due to diabetes increased over time in Montgomery County between 2010 and 2019. Among population subgroups, non-Hispanic Blacks have the highest ER visit rates followed by Hispanics, non-Hispanic Whites, and Asians. People aged 65 and older had the highest rate of emergency room visits due to diabetes. Geographically, residents from Upcounty, East County and Silver Spring had the highest rates of emergency room visits due to diabetes.
T2D develops over time when your body’s cells stop reacting to insulin in your pancreas. Glucose (sugar) stays in the blood and is not used as fuel for energy causing your blood sugar to rise or fall to dangerous levels. People who are more likely to have an unhealthy diet, inactive lifestyle, or experience social determinants of health such as inability to access healthy foods or low-income associated with unemployment or underemployment have an increased risk of developing T2D. Although the link between you and T2D could be hereditary, T2D can also result from complications associated with other health conditions.
In many instances, T2D can be prevented or successfully managed. Prevention can include lifestyle changes such regular exercise and physical activity, following a healthy eating plan, losing weight and keeping it off, or good mental health. The goal of T2D management is to maintain targeted blood glucose levels and prevent complications. T2D management includes taking medication as prescribed, regular doctor visits, regular exercise and physical activity, good mental health, and following a healthy eating plan.
Featured Programs

Learn about Diabetes
Learn about the different types of Diabetes and how it affects your health. Also, learn how to manage common symptoms and mental health with Diabetes.

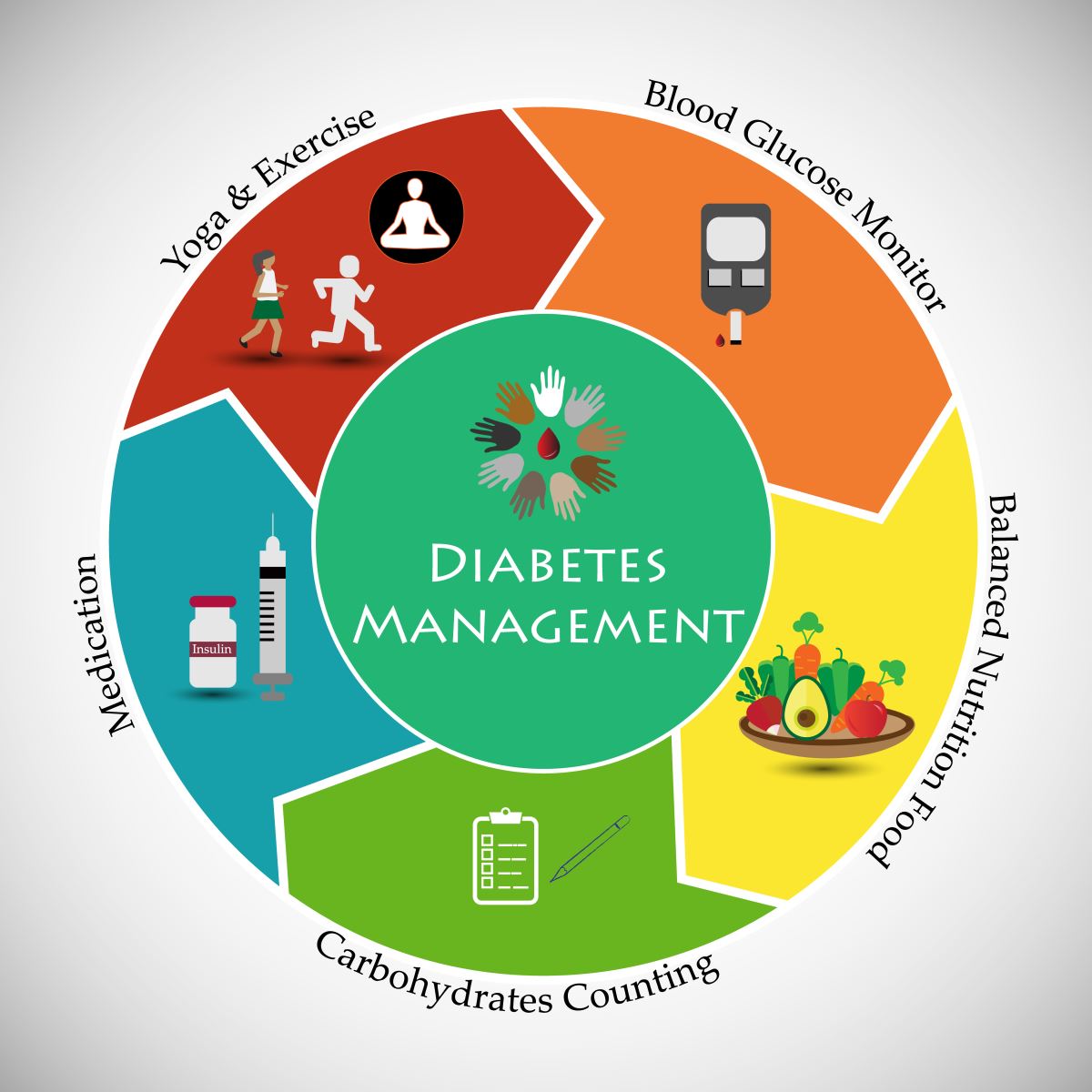
Managing Diabetes
Learn important Diabetes self-care activities to help you successfully manage your Diabetes. Learn about how Diabetes self-management classes can help you live a better and healthier lifestyle.
